SFDR Stands for Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation
SFDR is a set of frameworks outlining the incorporation of ESG criteria on a corporate and product level, assessing outcomes of the investment process on a sustainability scale.
SFDR in Detail
The EU Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation is only one part of a much bigger package that was adopted by the European Commission in 2018. Part of this, is also the EU Taxonomy Regulation (TR) and the EU Market in Financial Instruments Sustainable Preference Obligation (MiFID 2).
In particular, 2 different levels for the SFDR have been scheduled, the second of which taking place in January 2023.
Timeline of Implementation
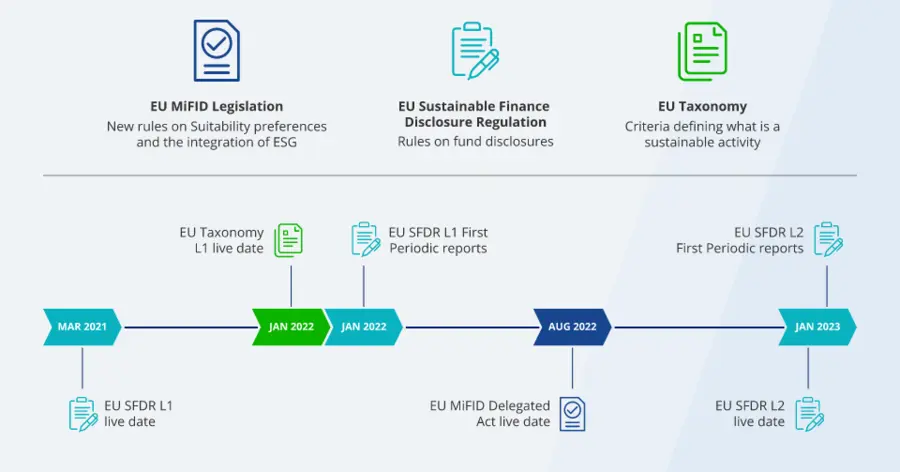
Source: J.P. Morgan Asset management, SFDR explained, 2022.
Purpose of SFDR
SFDR aims to redirect flows towards more sustainable investment solutions and at the same time to enhance transparency of sustainability of financial products and institutions. This second goal targets the so-called “greenwashing”.
What is greenwashing? The term is commonly used to refer to an organization’s false claims about an environmental positive impact that it is having. Although such claims could have some elements of truth, they have often misguided investors and other stakeholders.
The SFDR regulation forces market participants to disclose the ESG factors and sustainability characteristics of financial products like ETFs. It thus aids investors in determining the sustainability profile and risk of a fund, being also able to better compare different investment solutions with respect to ESG factors.
Classification
Under SFDR, UCITS funds can be classified under one of the following categories1:
What’s Next?
Investors’ interest and demand for sustainable investment solutions is projected to keep increasing in the years to come. Accordingly, the EU regulation will likely see new legislations being passed and new ESG disclosures will be made mandatory for asset managers and other market participants alike.